水平垂直居中
使用以下的核心代码,控制多行(多列)、单行(单列)的元素水平垂直居中
.container {
flex-direction: column; /* 这一行用于多行或多列的水平垂直居中,如果是单行单列可以去掉 */
align-items: center;
justify-content: center;
}页面效果如下:
<style>
* {
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
}
.container {
background: #f97897;
width: 600px;
height: 300px;
border-radius: 8px;
display: flex;
flex-direction: column;
align-items: center;
justify-content: center;
}
</style>
<div class="container">
<h1>多行水平垂直居中</h1>
<p>a very very very very very very very long text</p>
<p>some text</p>
</div>等高布局
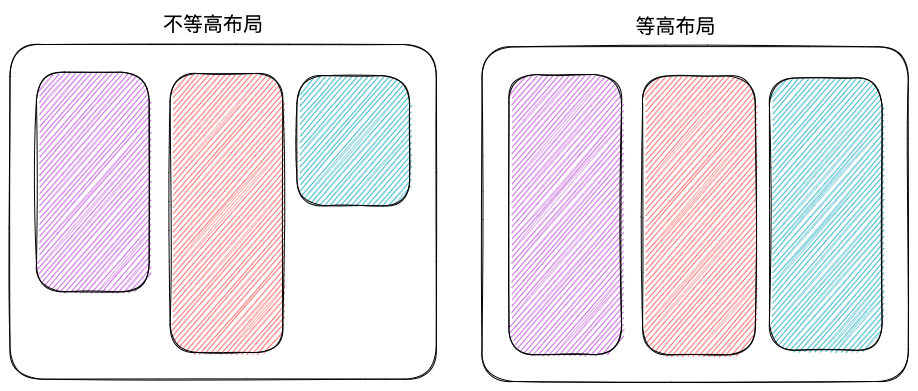
以下是浏览器中的效果
<style>
* {
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
}
.cards {
background-color: #009788;
color: #009788;
border-radius: 6px;
padding: 40px;
width: min(1024px, 100%);
display: flex;
flex-wrap: wrap;
gap: 1rem;
}
.card {
display: flex;
flex-direction: column;
flex: 1 1 300px;
border-radius: 4px;
background-color: #fff;
}
figure {
margin: 0;
background-color: #b1dfdb;
border-radius: 4px 4px 0 0;
display: flex;
justify-content: center;
margin-bottom: 16px;
overflow: hidden;
}
figure img {
max-width: 100%;
aspect-ratio: 16 / 9;
object-fit: cover;
object-position: center;
border-radius: 4px 4px 0 0;
mix-blend-mode: multiply;
transform-origin: center;
transform: scale3d(1, 1, 1);
transition: all 0.2s ease-in-out;
}
.card:hover img {
transform: scale3d(1.01, 1.02, 1.1);
}
.card > *:not(figure, button) {
padding: 0 1rem;
}
.card h3 {
font-size: 1.25em;
line-height: 1.5;
font-weight: 500;
letter-spacing: -0.02em;
margin-bottom: 1rem;
}
.card p {
flex: 1 1 auto;
font-size: 12px;
line-height: 1.625;
color: #467570;
font-weight: 300;
margin-bottom: 1rem;
}
.card button {
padding: 10px 18px 8px;
min-height: 44px;
font-size: 0.865em;
letter-spacing: 0.1em;
font-weight: bold;
text-transform: uppercase;
text-decoration: none;
color: #fff;
border-radius: 3px;
background: #009888;
transition: all 0.275s;
display: inline-flex;
justify-content: center;
align-items: center;
align-self: flex-start;
border: none 0;
margin: 1rem;
}
.card button:hover {
background: #095c53;
color: #fff;
text-shadow: 1px 1px 0 rgb(0 0 0 / 50%);
cursor: pointer;
}
</style>
<div class="cards">
<div class="card">
<figure>
<img src="https://loremflickr.com/640/480?random=1" alt="" />
</figure>
<h3>Bandwidth responsive web design.</h3>
<p>
Twitter stock equity vesting period learning curve launch party pitch
innovator series A financing churn rate handshake.
</p>
<button>Read more</button>
</div>
<div class="card">
<figure>
<img src="https://loremflickr.com/640/480?random=3" alt="" />
</figure>
<h3>Social media accelerator.</h3>
<p contenteditable>
Churn rate non-disclosure agreement buyer focus ecosystem iPad.(Please
click on me to add content!)
</p>
<button>Read more</button>
</div>
<div class="card">
<figure>
<img src="https://loremflickr.com/640/480?random=2" alt="" />
</figure>
<h3>Marketing iPad angel investor.</h3>
<p>
Funding influencer partner network metrics bandwidth leverage traction
buzz virality.
</p>
<button>Read more</button>
</div>
</div>等分列布局
常常用在移动端的 Footer Nav 中
主要是通过一下的代码实现等分列。默认情况下设置flex:1的 flex 项目在收缩的时候,
其宽度不会小于最小内容尺寸min-content,如果要改变这点,
则需要显式设置min-width | min-inline-size | min-heigh| min-block-size为 0,来覆盖min-content。
但是因为设置了flex: 1(主要是里面的flex-grow: 1),它会让 flex 项目按照扩展因子自动分配剩余空间
.item {
flex: 1; /* 同 flex: 1 1 0%; */
min-width: 0;
}复制以下代码到浏览器查看效果
<style>
* {
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
}
.device {
display: flex;
flex-direction: column;
width: 100%;
min-height: 100vh;
}
header {
height: 80px;
background-color: #e23455;
}
main {
flex: 1 1;
overflow: auto;
}
footer {
display: flex;
align-items: center;
padding: 20px;
background-color: #e23455;
}
footer .item {
flex: 1; /* 同 flex: 1 1 0%; */
min-width: 0;
text-align: center;
}
</style>
<div class="device">
<header>Header</header>
<main>
<p>a long text</p>
<p>a long text</p>
<p>a long text</p>
<p>a long text</p>
<p>a long text</p>
</main>
<footer>
<div class="item">
<div>图片</div>
<div>首页</div>
</div>
<div class="item">
<div>图片</div>
<div>分类</div>
</div>
<div class="item">
<div>图片</div>
<div>消息</div>
</div>
<div class="item">
<div>图片</div>
<div>购物车</div>
</div>
<div class="item">
<div>图片</div>
<div>我的xxxxxxx</div>
</div>
</footer>
</div>圣杯布局
圣杯布局由以下几个部分组成
- 页头
- 页脚
- 主内容
- 左侧边栏
- 右侧边栏
它需要当 css 未加载时主内容要位于两个边栏之前显示,也就是内容优先,所以可以用到order: -1来控制主内容在 flex 布局中的排序
<style>
* {
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
}
.home-page {
display: flex;
flex-direction: column;
width: 100%;
min-height: 100vh;
}
header {
height: 80px;
background: #e289e2;
}
main {
flex: 1 1 100%;
display: flex;
}
aside:nth-of-type(1) {
width: 200px;
background: #dd3;
order: -1;
}
article {
flex: 1 1 auto;
}
aside:nth-of-type(2) {
width: 300px;
background: #aeee;
}
footer {
height: 80px;
background: #d43d;
}
</style>
<div class="home-page">
<header>header</header>
<main>
<article>
<!-- 内容列 -->
a very long text
</article>
<aside>导航栏</aside>
<aside>右侧内容栏</aside>
</main>
<footer>footer</footer>
</div>sticky-footer 布局
该布局就是内容高度不够时,内容自动填充,footer 位于底部。但是当内容超过当前视口高度,则 footer 和内容也会随之滚动。
具体效果请看一下代码
<style>
* {
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
}
.home-page {
width: 100vw;
height: 100vh;
overflow-x: hidden;
display: flex;
flex-direction: column;
}
header,
footer {
height: 80px;
flex-shrink: 0;
}
main {
flex: 1 0 auto;
min-height: 0;
/* flex: 1 1 auto; */
}
</style>
<div class="home-page">
<header>header</header>
<main>
<p>a long text</p>
<p>a long text</p>
<p>a long text</p>
<p>a long text</p>
<p>a long text</p>
<p>a long text</p>
<p>a long text</p>
<p>a long text</p>
<p>a long text</p>
<p>a long text</p>
<p>a long text</p>
<p>a long text</p>
<p>a long text</p>
<p>a long text</p>
<p>a long text</p>
<p>a long text</p>
<p>a long text</p>
<p>a long text</p>
<p>a long text</p>
<p>a long text</p>
<p>a long text</p>
<p>a long text</p>
<p>a long text</p>
<p>a long text</p>
<p>a long text</p>
<p>a long text</p>
<p>a long text</p>
<p>a long text</p>
<p>a long text</p>
<p>a long text</p>
<p>a long text</p>
<p>a long text</p>
<p>a long text</p>
<p>a long text</p>
<p>a long text</p>
<p>a long text</p>
<p>a long text</p>
<p>a long text</p>
<p>a long text</p>
<p>a long text</p>
<p>a long text</p>
<p>a long text</p>
<p>a long text</p>
<p>a long text</p>
<p>a long text</p>
<p>a long text</p>
<p>a long text</p>
<p>a long text</p>
<p>a long text</p>
<p>a long text</p>
<p>a long text</p>
<p>a long text</p>
<p>a long text</p>
<p>a long text</p>
</main>
<footer>footer</footer>
</div>

