首先,我们需要知道 redux 的相关概念
概念
首先,我们需要知道 redux 有以下概念
Action:一个 JavaScript 对象,描述动作相关信息,必须要包含的是一个 type 属性,用于描述当前 Action,其他属性为值。
Reducer:定义应用状态如何响应不同动作(action),如何更新状态;
Store:管理 action 和 reducer 及其关系的对象,主要提供以下功能:
- 维护应用状态并支持访问状态(getState());
- 支持监听 action 的分发,更新状态(dispatch(action));
- 支持订阅 store 的变更(subscribe(listener));
下面是我画的一个流程图
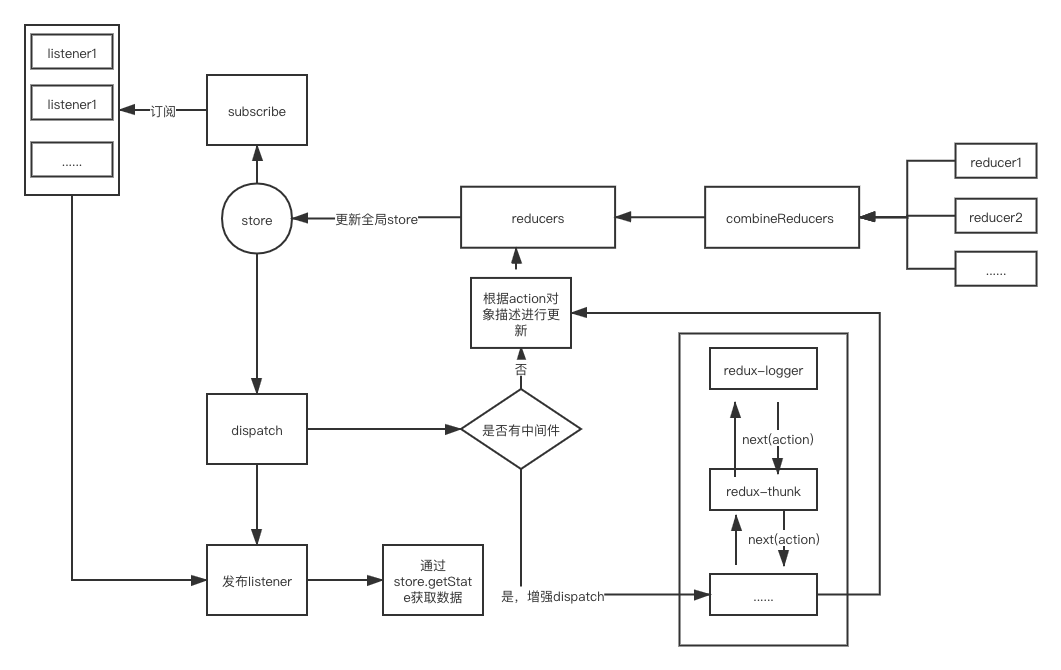
我使用的是
npm run build后的代码讲解的
createStore
先从createStore的源码说起,我们看如下的源码:
// 只传两个参数的,且第二个参数为函数时,作为enhancer
if (typeof preloadedState === "function" && typeof enhancer === "undefined") {
enhancer = preloadedState;
preloadedState = undefined;
}
if (typeof enhancer !== "undefined") {
if (typeof enhancer !== "function") {
throw new Error("Expected the enhancer to be a function.");
}
// 则enhancer就是 applyMiddleware 的返回值,enhancer也是一个高阶函数
return enhancer(createStore)(reducer, preloadedState);
}以上的代码是为 applyMiddleware(自定义中间件) 服务的,如果增加了自定义中间件会进入 enhancer 分支,对 dispatch 进行增强。enhancer 会在后面说到
然后,我们看一下在 createStore 中的局部变量
// currentReducer必须是一个函数,用来定义响应不同action
var currentReducer = reducer;
// 更新后的state
var currentState = preloadedState;
var currentListeners = [];
// nextListeners 则是存放 监听器 的变量
var nextListeners = currentListeners;
var isDispatching = false;以上,主要的是currentReducer、currentState和nextListeners。
它们的作用分别是:
currentReducer: 保存传入到 createStore 的 reducer
currentState: 更新后的值,getState 方法获取的就是这个局部变量
nextListeners: 当使用 subscribe 来注册一个监听器的时候,都会被 push 到这里,并且 dispatch 时,会调用执行所有的监听器
getState
这个方法比较简单,它只获取 createStore 中的局部变量 currentState, 也就是我们的全局 store
function getState() {
if (isDispatching) {
throw new Error(
"You may not call store.getState() while the reducer is executing. " +
"The reducer has already received the state as an argument. " +
"Pass it down from the top reducer instead of reading it from the store."
);
}
return currentState;
}subscribe
redux 采用的是发布-订阅模式来监听 store 的变化,subscribe 则是一个订阅函数。
function subscribe(listener) {
var isSubscribed = true;
ensureCanMutateNextListeners();
nextListeners.push(listener);
return function unsubscribe() {
if (!isSubscribed) {
return;
}
isSubscribed = false;
ensureCanMutateNextListeners();
var index = nextListeners.indexOf(listener);
nextListeners.splice(index, 1);
currentListeners = null;
};
}他会将注册的监听器存放到 nextListeners中,可以通过 unsubscribe 来注销监听器。
而在 nextListeners 中的监听器,都会在 dispatch 时被调用,在这之后使用 getState 获取到的都是更新后的 store。在react-redux中就是通过在 Provider 中使用 subscribe 注册监听器,然后在监听器中获取到更新后的 store 进行派发。
dispatch
以下是 dispatch 中组要的逻辑
try {
isDispatching = true;
// 接收到 combination 计算的值后,更新 currentState
currentState = currentReducer(currentState, action);
} finally {
isDispatching = false;
}
// 获取 nextListeners 中的 监听器
var listeners = (currentListeners = nextListeners);
// 遍历并执行通过subscribe订阅的监听器
for (var i = 0; i < listeners.length; i++) {
var listener = listeners[i];
listener();
}dispatch 则是根据 action 来执行 reducer 中不同的更新逻辑,然后返回最新的 store,并且执行监听器(发布)。这样,就可以获取到最新的 store 来做相应的更新操作。
当然,一般的业务中,通常会有多个 reducer,这个时候就需要通过 combineReducer 来合并多个 reducer。它的主要逻辑如下:
// 接收 old state 和 描述action的对象
return function combination(state, action) {
if (state === void 0) {
state = {};
}
// .......
var hasChanged = false;
var nextState = {};
for (var _i = 0; _i < finalReducerKeys.length; _i++) {
// _key 是 每个reducer对应的key,
// 如: combineReducers({ toDo: todoReducer })
// _key 就是 toDo
// reducer 就是 todoReducer
var _key = finalReducerKeys[_i];
var reducer = finalReducers[_key];
var previousStateForKey = state[_key];
// 开始执行项目中定义的reducer,并且传入old state中对应的reducer的值
// nextStateForKey 就是新的值
var nextStateForKey = reducer(previousStateForKey, action);
// 更新全局store上的当前action对应的state
nextState[_key] = nextStateForKey;
hasChanged = hasChanged || nextStateForKey !== previousStateForKey;
}
// 判断是否有变化
hasChanged =
hasChanged || finalReducerKeys.length !== Object.keys(state).length;
// 如果有变化,则采用 nextState,如果没有则返回old state
return hasChanged ? nextState : state;
};这就是在使用 combinerReducer时返回的新的 reducer。在每一次更新时,都会进行一次遍历,来对比相应 reducer 中的 state 是否发生变化。更新则采用 nextState,否则返回 old state。
applyMiddleware
中间件的作用就是增强 dispatch 的功能,常见的有 redux-logger、redux-thunk等等。
redux-logger: 支持在 dispatch 时输出更改前后更改后的数据
redux-thunk: 则是支持 dispatch 一个函数,这可以完成一个控制反转,来使 dispatch 支持异步调用。
// applyMiddleware 是一个高阶函数
function applyMiddleware() {
// 使用如下中间件
// applyMiddleware(logger, thunk)
// 则 middlewares = [logger, thunk]
for (
var _len = arguments.length, middlewares = new Array(_len), _key = 0;
_key < _len;
_key++
) {
middlewares[_key] = arguments[_key];
}
// 返回一个enhancer,也就是createStore的第三个参数
return function (createStore) {
return function (reducer, preloadedState) {
// 通过高阶函数,store的权限交出
var store = createStore(reducer, preloadedState);
var _dispatch = function dispatch() {
throw new Error(
"Dispatching while constructing your middleware is not allowed. " +
"Other middleware would not be applied to this dispatch."
);
};
var middlewareAPI = {
getState: store.getState,
dispatch: function dispatch(action) {
for (
var _len2 = arguments.length,
args = new Array(_len2 > 1 ? _len2 - 1 : 0),
_key2 = 1;
_key2 < _len2;
_key2++
) {
args[_key2 - 1] = arguments[_key2];
}
return _dispatch.apply(void 0, [action].concat(args));
},
};
var chain = middlewares.map(function (middleware) {
// 遍历并调用中间件,传入由 middleware 控制的getState和dispatch
// 每一个middleware应该也是一个高阶函数
return middleware(middlewareAPI);
});
// chain就是每个中间件return的第二层函数
// compose会从右到左,执行所有中间件。直到执行到最开始的一个中间件中
// 然后返回一个新的dispatch, 这个dispatch 就是中间件代码中最深层的匿名函数了 return (action) => {}
_dispatch = compose.apply(void 0, chain)(store.dispatch);
// 返回一个增强 dispatch 后的 store
// 然后再调用 dispatch 时,会按照中间件的顺序执行,然后中间件中通过next,进入下一个中间件中(进入调用栈),然后出栈,这个时候,获取到的state为新的值
return _objectSpread2(
_objectSpread2({}, store),
{},
{ dispatch: _dispatch }
);
};
};
}applyMiddleware 机制的核心在于组合 compose,将不同的 middleware 一层一层包裹到原生的 dispatch 之上,而为了方便进行 compose,需对 middleware 的设计采用柯里化 curry 的方式,达到动态产生 next 方法以及保持 store 的一致性。由于在 middleware 中,可以像在外部一样轻松访问到 store, 因此可以利用当前 store 的 state 来进行条件判断,用 dispatch 方法拦截老的 action 或发送新的 action。
总结:
- redux 采用的是发布订阅模式
- dispatch 会触发 linsters
- middleware 的设计则采用柯里化,达到动态产生 next 方法以及保持 store 的一致性,避免多个 middleware 产生嵌套。


